Apoptosis Assays
Our scientific team are experts in guiding which apoptosis/cell viability assays might be more suitable for your project objective
Cancers are known to exhibit resistance to conventional treatments, which contribute to relapses and disease progression. Quantification of the proportion of cells surviving a treatment is performed through cell viability assays. Screening for compound toxicity is a fundamental step in analysing the cytotoxic capability of a compound towards cancer cells.
Many of the in-house assays measure cell death based on compromised cell membrane in response to drug treatment.
For instance, LDH assays measure enzymatic activity that is released into the reaction mixture by cells undergoing cell death.
Cell viability is routinely measured using the MTT assay which involves the conversion of the water-soluble MTT substrate into formazan salts by actively metabolising cells.
CellTiter Glo/Fluor is an alternative means of determining cell viability. Unlike MTT assay, this approach uses live-cell measurements by employing fluorogenic substrate that is proteolytically cleaved following entry into viable cells. The fluorescent signal emitted is proportional to the number of living cells.
Alternatively, CellToxTM Green Cytotoxicity Assay involves binding of reporter molecules to released DNA and the fluorescence serves as a parameter to measure the amount of cell death post-treatment.
Caspase 3/7 Assay
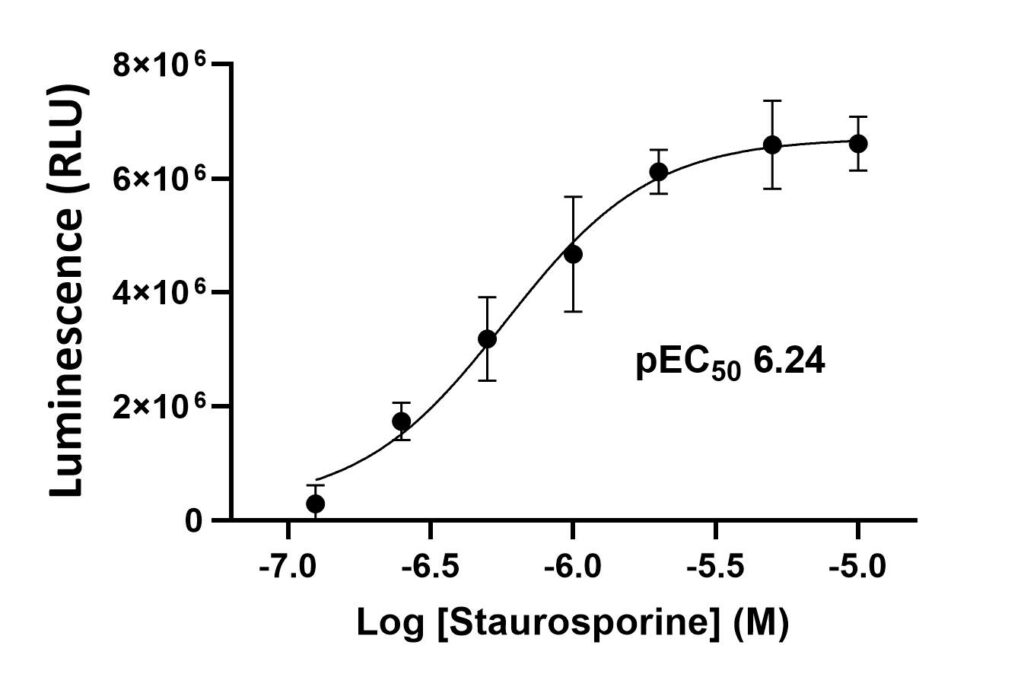
Measurement of Caspase 3/7 activity in HeLa cells treated with Staurosporine for 4 hours. The Caspase-Glo 3/7 Reagent was added directly to cells in 96-well plates and incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes before recording luminescence (RLU). Each point represents the average of 3 replicates (error bars represent ±SEM).
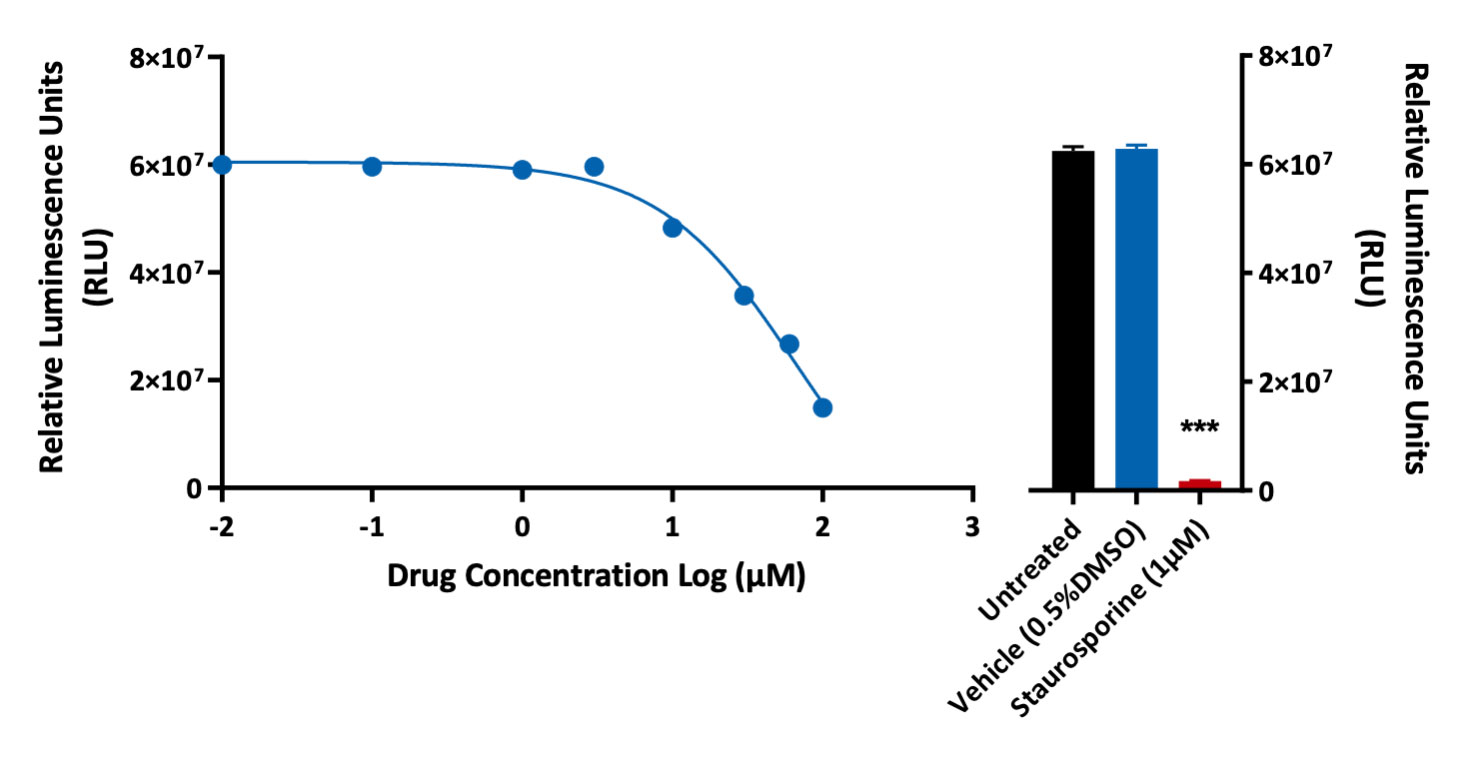
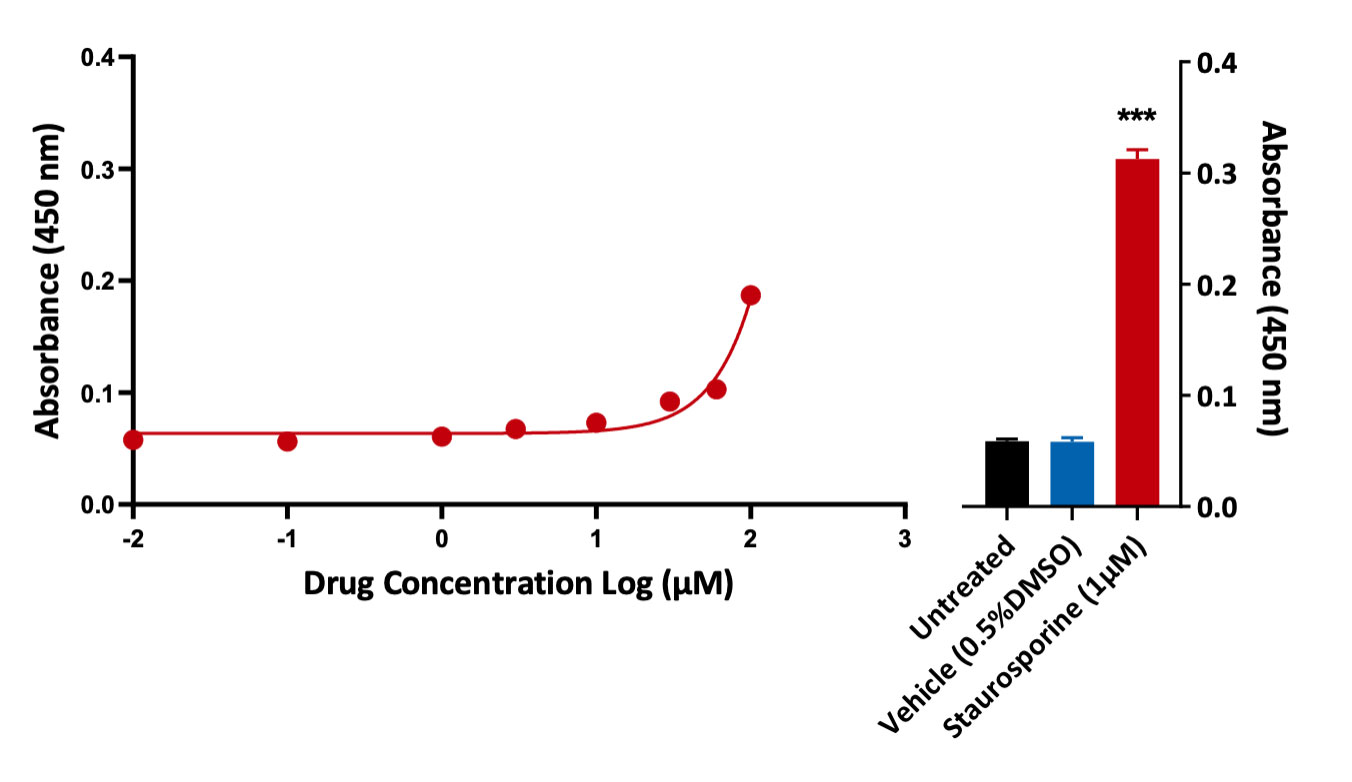
Measurement of viability and cytotoxicity. Cell Viability and cytotoxic responses were assessed in A549 (lung cancer cell line) using the CellTitre-Glo and LDH assays. Staurosporine (positive control compound) induced a significant reduction in cell viability when compared to untreated or vehicle control (***p<0.001; ±SEM).
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your project and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.