Inflammation Assays
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
IBD is a term used to describe disorders that involve chronic/recurrent inflammation of the colon and small intestine.
Ulcerative colitis is mainly localised into the colon (large intestine), while Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the digestive system. In both cases, symptoms may range from mild to severe, with periods of active illness followed by temporary remission. There is currently no cure for IBD, and medications tend to reduce the symptoms preventing severe complications, which include colon cancer.
Causes:
- Defects in the intestinal barrier
- Impaired immune function
- Genetic predispositions (e.g. NOD2 mutation)
- Environmental factors
Characteristics:
- Increased proinflammatory immune response
- Increased permeability of the intestinal epithelial barrier
- Increased mucus production
- Rearrangement of tight junction proteins
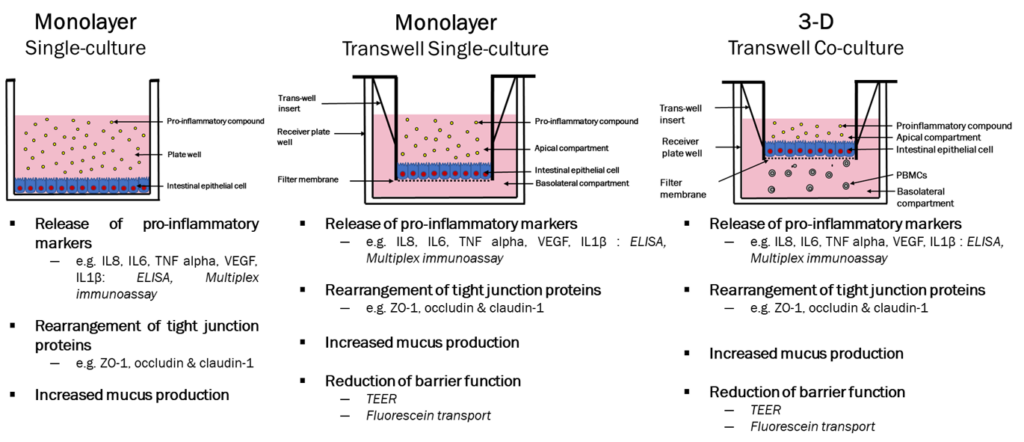
In vitro models –
Relevant cell types:
- Caco-2 cells – Human Colorectal adenocarcinoma epithelial-like cell line
- InEpC – Primary Human Intestinal Epithelial Cells
- Immune cells – Freshly isolated from peripheral blood of healthy/diseased volunteers
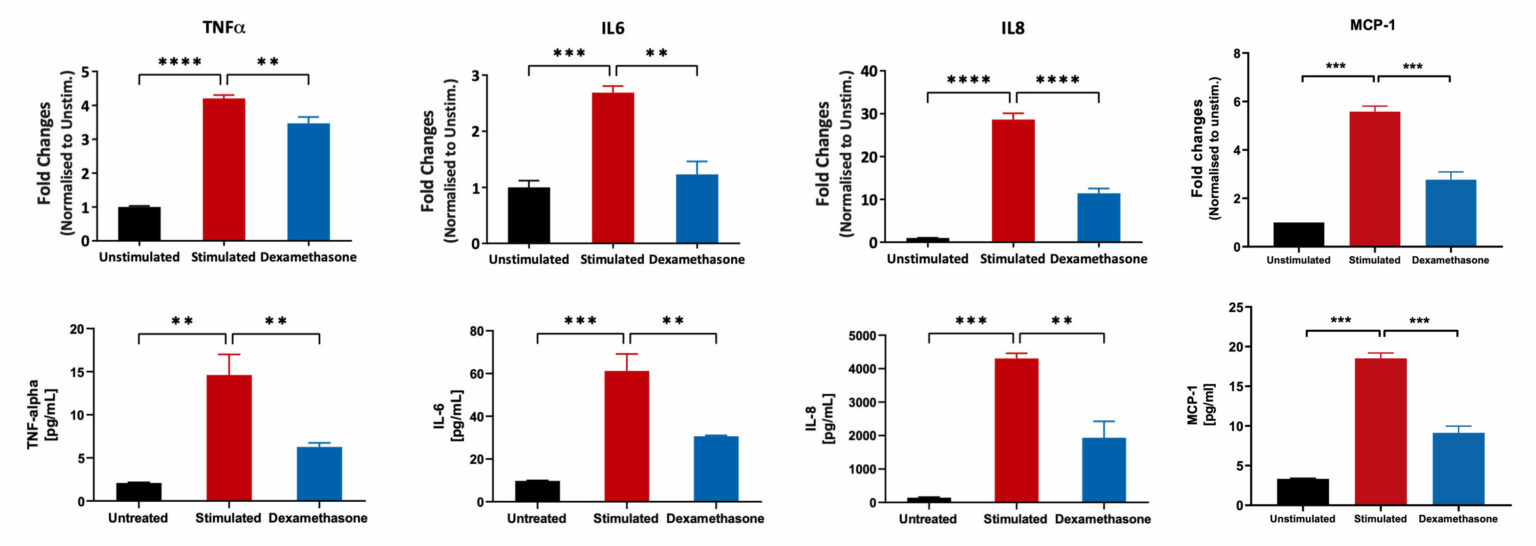
Caco-2 Model for IBD: Inflammatory Mediators
Caco-2 cells were differentiated for 21 days and subsequently treated with Dexamethasone, followed by stimulation with LPS+ IL1beta cocktail. mRNA expression in cell lysates was quantified using the Luminex Quantigene™ Assay. The supernatants were analysed for inflammatory mediators using a Luminex Multiplex Assay (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001; n=3 mean±SEM).
Pro-inflammatory marker suppression by Sulfasalazine and 5-Aminosalicylic Acid
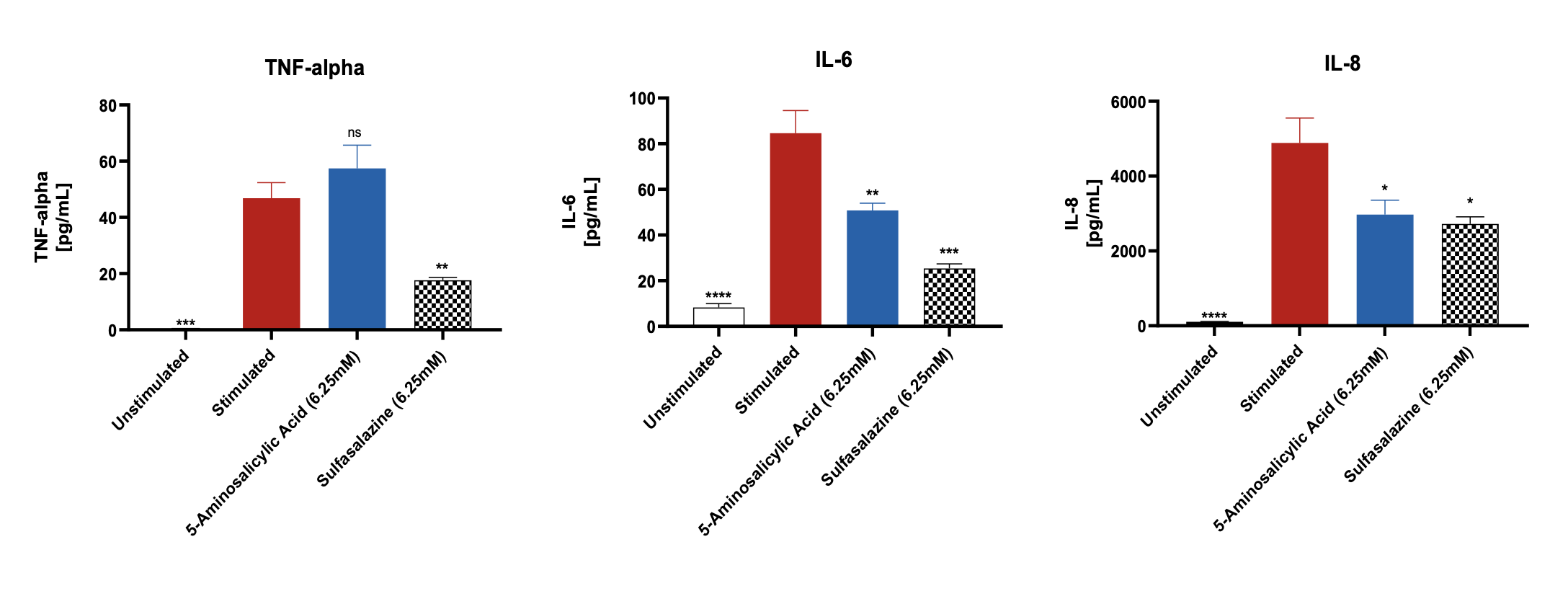
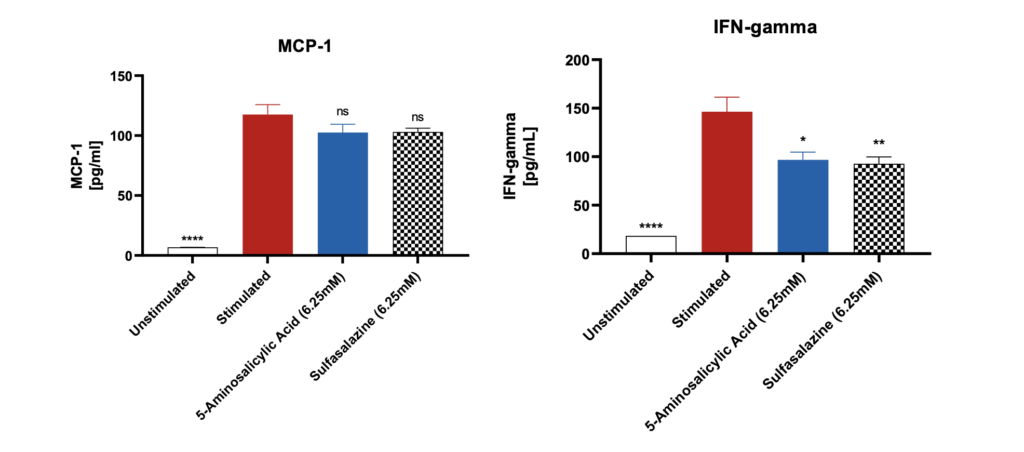
Significantly increased levels of pro-inflammatory markers were observed after stimulation of the differentiated Caco-2 monolayers with IL-1β and LPS when compared to unstimulated control. The levels of these markers were suppressed when the Caco-2 monolayers were pre-treated with the reference compounds. Data was analyzed using Ordinary One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test [95% CI of diff.] (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns= not significant). All the conditions were compared to the stimulated control for each of the markers and showed significant differences.
Note: Unstimulated = Co-culture (Caco-2 +THP-1), Stimulated= Co-culture (Caco-2 +THP-1) + LPS + IL-1β.
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) release by Caco-2 cells
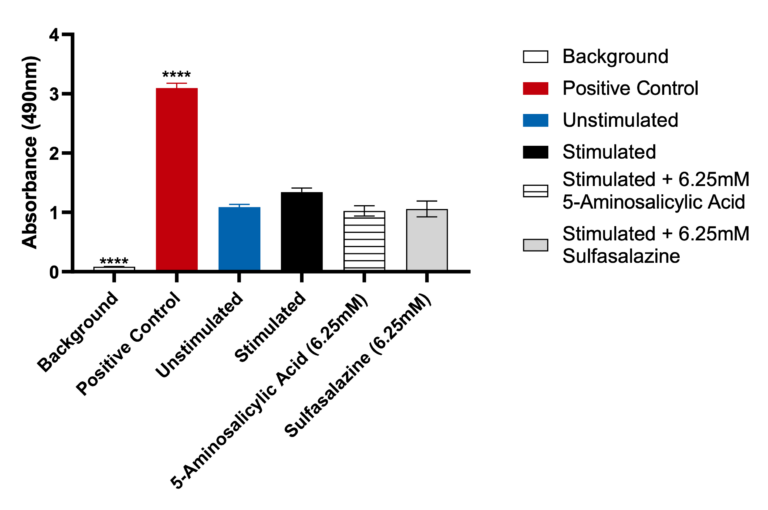
Data was analyzed using Ordinary One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test [95% CI of diff.] (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ns= not significant). The LDH positive control, provided with the assay, generated significant OD 450 values (p<0.0001) compared to the unstimulated control. Both Sulfasalazine and 5-Aminosalicylic Acid showed no significant LDH release when compared to the unstimulated control.
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your project and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.