Migration Assays
Our scientists at Cellomatics specialise in a range of migration assays.
Our scientists at Cellomatics specialise in a range of migration assays.
Cancer disease management is often plagued by metastasis (migration) of cancer cells to distant locations from the primary growth site and invading into nearby tissues to establish secondary tumours. Disabling cell motility is one strategy to delay disease progression. In vitro analysis of migration and/or proliferation can me modelled using wound healing assays. In this protocol a scratch is introduced on a pre-formed monolayer of adherent cells. The duration from drug treatment to closure of the gap then provides an indication of the drug’s efficiency at inhibiting cellular movement.
Transwell systems also allow quantification of cell migration following drug treatment between the apical and basal chambers across a membrane, mimicking physiological conditions. This method has been employed for our suspension cell lines wherein movement between the two compartments is mediated by chemoattractants.
Get in touch to find out more about the migration assays we offer at Cellomatics.
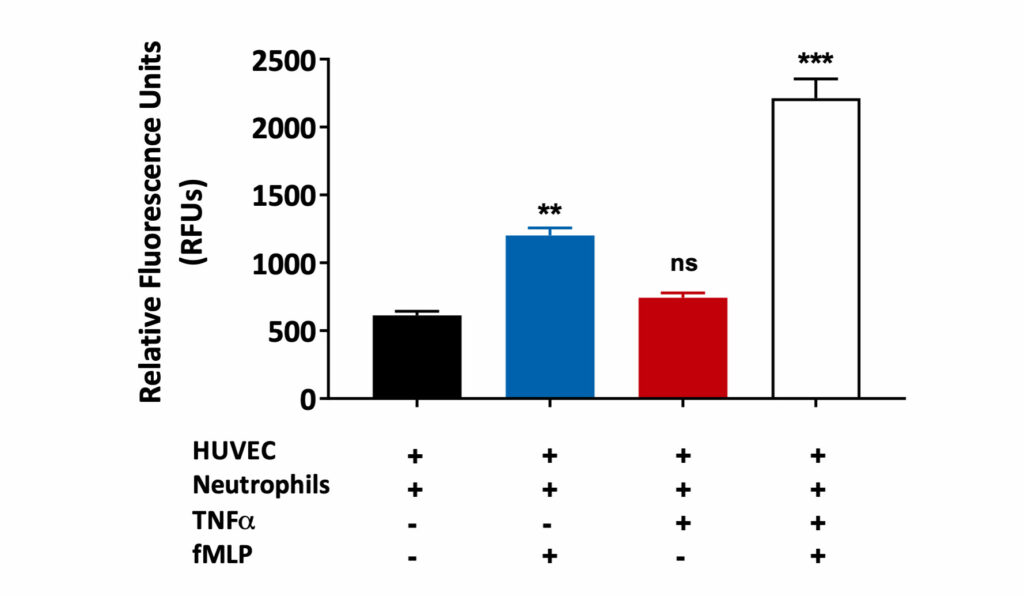
Neutrophil migration through the HUVEC monolayer
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were grown on a transwell insert and stimulated with TNFα in the presence or absence of fMLP (a chemoattractant). Peripheral blood derived human neutrophil transmigration through the HUVEC monolayer was measured and expressed as Relative Fluorescence Units (RFU). A statistically significant increase in human neutrophil migration towards fMLP was observed in HUVEC monolayers treated with TNFα when compared to untreated HUVEC monolayers. This is suggestive of TNFα induced HUVEC barrier permeability. (ns=not significant; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001±SEM).
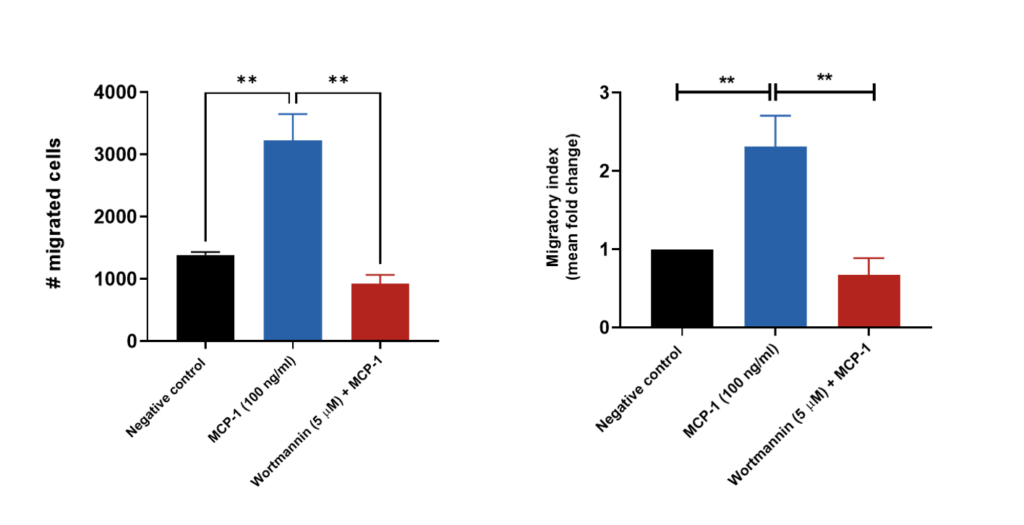
THP-1 migration induced by MCP-1/CCL2
THP-1 cells were stained with Calcein AM and added to the top chamber of the transwell. MCP-1 was then added to the bottom chamber in the presence or absence of Wortmannin (PI3K inhibitor). At the end of the 2 hour migration, the number of cells that migrated into the basal chamber of the experimental set-up was quantified using the JuLITM Stage imaging platform. Relative fold-changes were determined for each treatment condition using the negative (untreated) condition as a baseline. Wortmannin serves as a positive control for the inhibition of THP-1 migration. Each condition is representative of three independent biological repeats (**p<0.05, n=3±SEM). MCP-1 induced the migration of THP-1 cells, having an estimated and significant two-fold-change increase relative to the untreated condition (negative control), suggesting its suitability as a chemoattractant for these cells. Treatment of THP-1 cells with the PI3K enzyme inhibitor Wortmannin resulted in a significant reduction in cell migration when compared to the MCP-1 only condition.
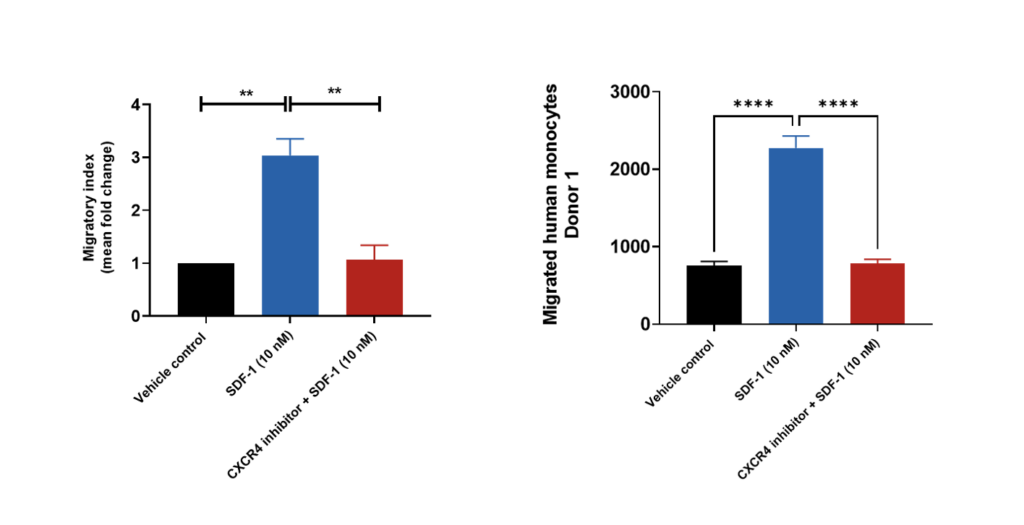
Primary monocyte migration induced by SDF-1
Human peripheral blood derived CD14+ monocytes were stained with Calcein AM and added to the top chamber of the transwell. SDF-1 (also known as CXCL12) was then added to the bottom chamber in the presence or absence of CXCR4 antagonist (the receptor for SDF-1). At the end of the 4 hour migration, the number of cells that migrated into the basal chamber of the experimental set-up was quantified using the JuLITM Stage imaging platform. Relative fold-changes were determined for each treatment condition against the Vehicle control. Each condition is representative of three independent biological repeats (**p<0.05, n=3±SEM). SDF-1 induced the migration of CD14+monocytes suggesting its suitability as a chemoattractant for these cells. Treatment of CD14+monocytes with CXCR4 antagonist resulted in a significant reduction in SDF-1 induced cell migration.
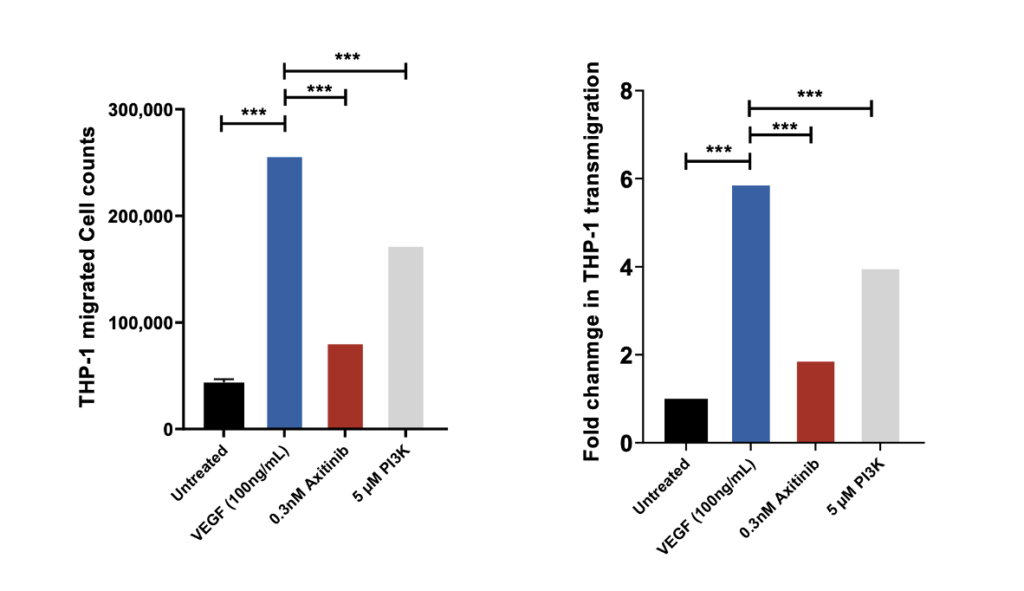
THP-1 trans migration across HUVEC monolayer induced by VEGF
THP-1 migrated cell counts for the 4 control conditions: untreated, VEGF-165 treated, Axitinib (a tyrosine kinase inhibitor) and PI3K Inhibitor.
THP-1 migrated cell counts are indicative of the number of THP-1 cells which have passed through the HUVEC monolayer into receiver wells as a direct measure of the permeability of the HUVEC monolayer following drug treatment. Axitinib/VEGF-165 and PI3Kinhibitor/VEGF-165 co-treatment demonstrates significant inhibition of MCP-1 induced transmigration of THP-1 cells suggesting inhibition of HUVEC monolayer permeability. Each condition is representative of three technical replicates (n=3); mean ± SEM.

Peripheral blood neutrophil migration induced by IL8
Human peripheral blood derived neutrophils were stained with Calcein AM and added to the top chamber of the transwell. Recombinant IL8 was then added to the bottom chamber as a chemoattractant. At the end of the 90 minutes migration, the number of cells that migrated into the basal chamber of the experimental set-up was quantified using the imaging platform. Each condition is representative of three independent biological repeats (**p<0.05, n=3±SEM).
Chemokinesis

A scratch wound was created on a confluent A549 cell (lung carcinoma) monolayer and treated with Olaparib (Ola; a PARP inhibitor), 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU; causes DNA damage); a combination 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) and Olaparib (Ola)(5-FU + Ola). Images were acquired using live imaging platform at the indication time points (hours). The wound size/scratch was measured at all time points. The wound closure percentage was analysed assuming 0% closure at 0 hours, and calculating all the following time points as ratio to 0 hours [*p<0.05; **p<01; ***p<0.001; ± SEM].
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your project and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.