Respiratory Assays
Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the commonest interstitial lung disease (ILD) and is characterised by progressive scarring of the lungs. An impaired pulmonary wound healing response following lung injury coupled with excessive production of collagens leads to a pathogenic lung fibrosis.
Inflammatory mediators
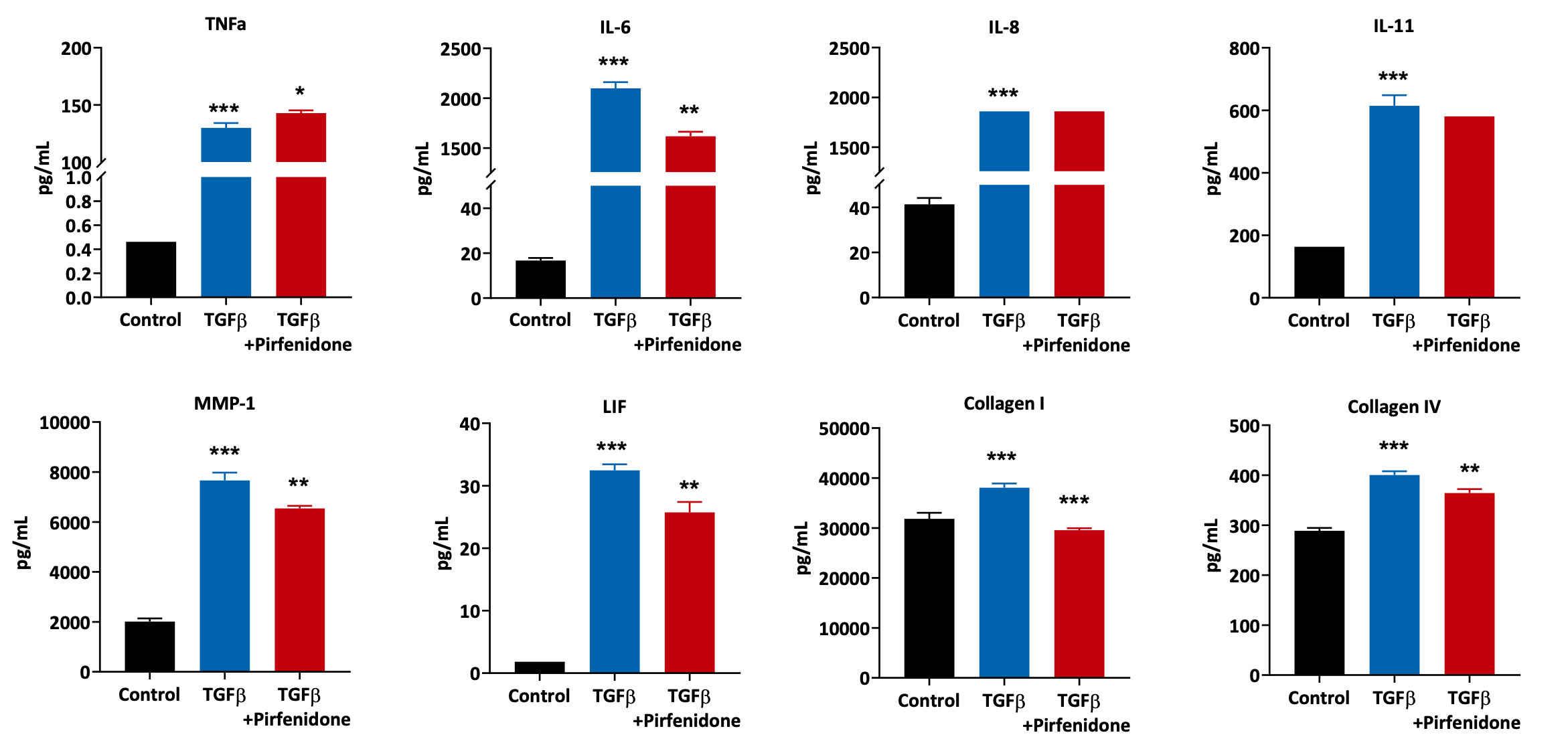
Primary Human Lung Fibroblasts were pre-treated with Pirfenidone for 1 hour followed by 24 hours stimulation with TGFβ. Supernatants were analysed using Luminex multiplexed assays for inflammatory and extracellular matrix component markers. All treatment conditions were compared to the TGFβ treated samples (***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.05; n=3±SEM).
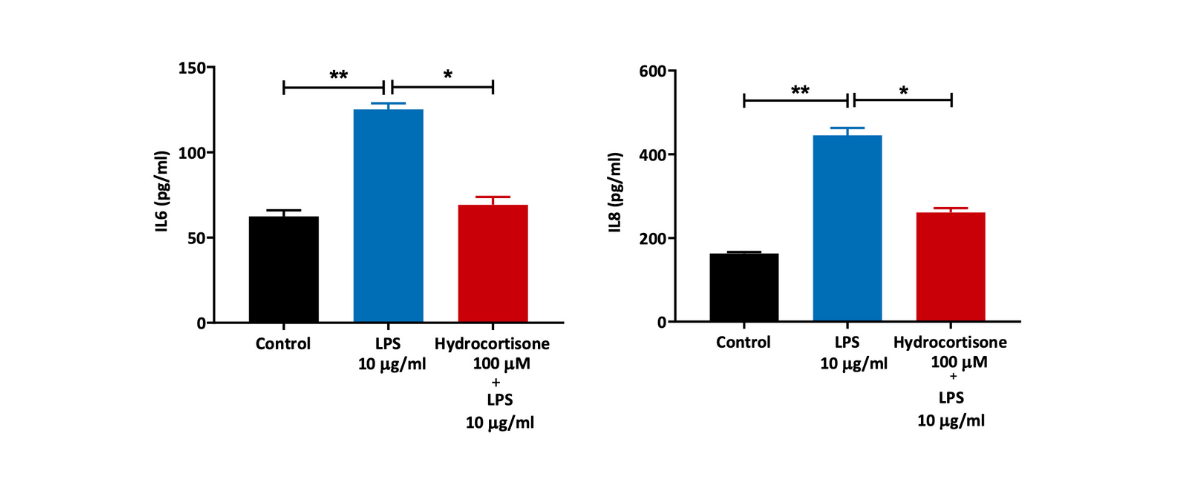
Human Lung Fibroblasts stimulated with LPS
Primary Human Lung Fibroblasts were treated with 10 µg/ml LPS for 24 hours in the presence or absence of reference compound (hydrocortisone). Cell culture supernatants were then collected and levels of the proinflammatory IL6 and IL8 measured by ELISA (n=5±SEM; *p<0.05; **p<0.01).
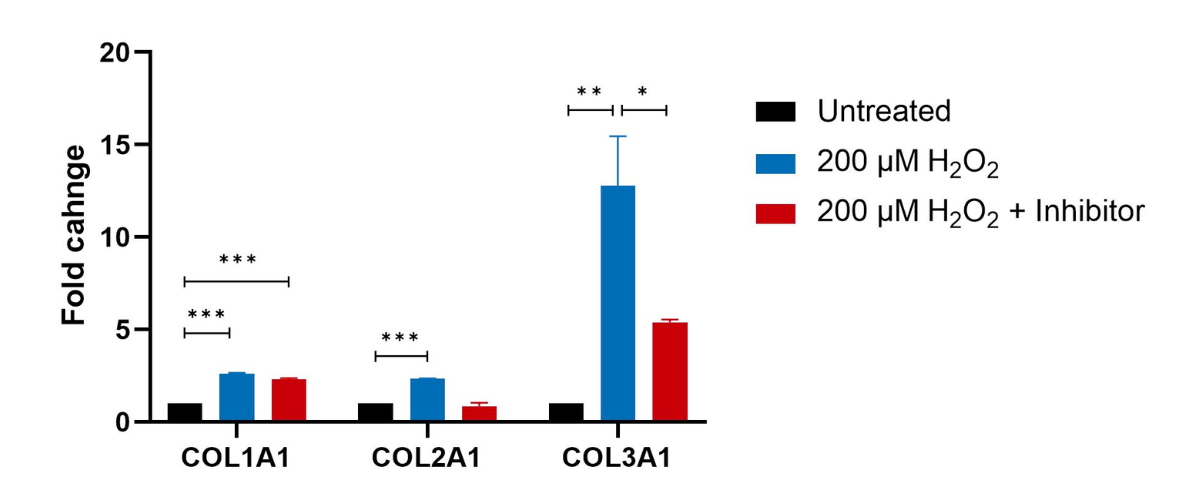
Collagen biomarkers in Human Lung Fibroblasts
Primary Human Lung Fibroblasts were pre-treated with Pirfenidone (Targeting the inflammasome and down regulating TGFβ) for 1 hour followed by 24 hours stimulation with H2O2. Cell lysates were analysed using QuantiGene multiplex to detect changes in Collagen genes. Fold changes were determined by normalising target gene expression to house keeping genes (GAPDH and HPRT1). Treatment conditions were compared to the H2O2 treated samples (***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.05; n=3±SEM).
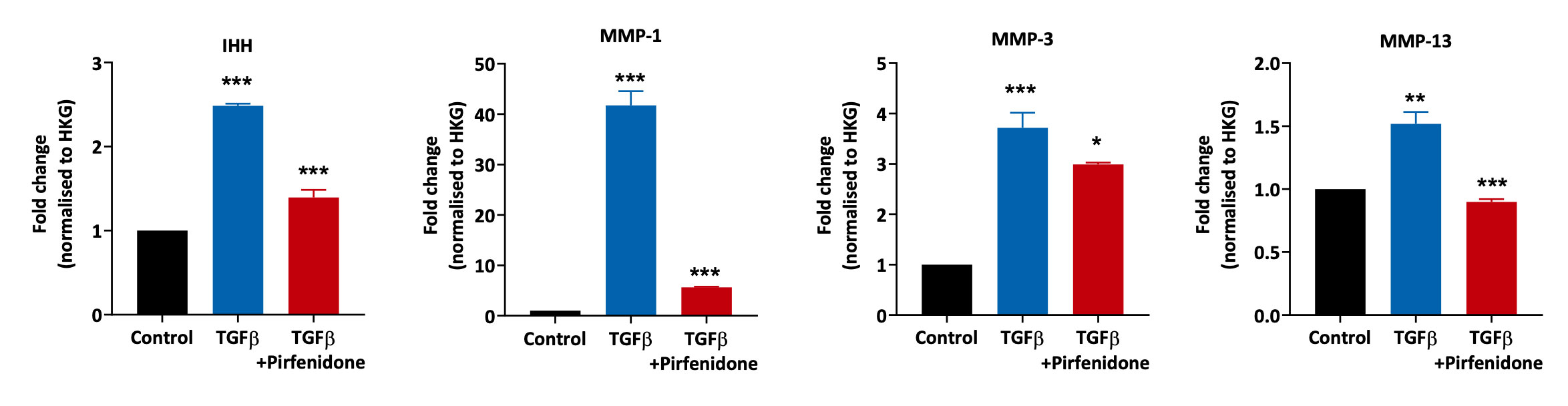
Extracellular Matrix Deposition
Primary Human Lung Fibroblasts were pre-treated with Pirfenidone for 1 hour followed by 24 hours stimulation with TGFβ (to drive the fibrotic pathway). Cell lysates were analysed using QuantiGene multiplex to detect changes in extracellular matrix component genes. Fold changes were determined by normalising target gene expression to house keeping genes (GAPDH and HPRT1). All treatment conditions were compared to the TGFβ treated samples (***p<0.001; **p<0.01; *p<0.05; n=3±SEM).
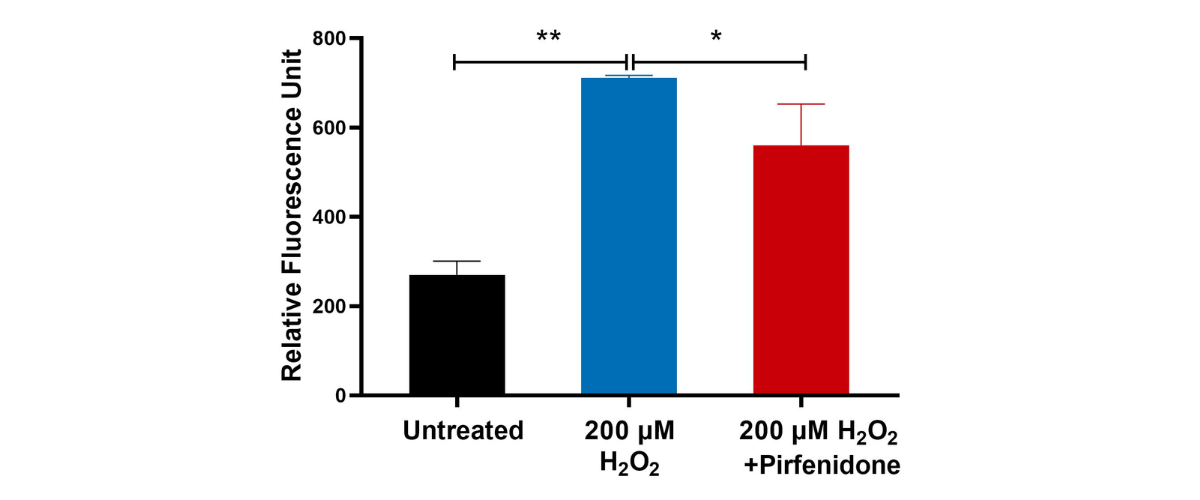
Oxidative Stress - Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)
Human Lung Fibroblasts were pre-treated with Pirfenidone as an inhibitor for 1 hour followed by treatment with 200 µM H2O2 for 48 hours. Lysates were analysed for intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) using a fluorescence detection kit. A significant increase in intracellular ROS (indicated by increased fluorescence signal) was observed in 200 µM H2O2 when compared to untreated controls. (n=3±SEM; **p<0.01).
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your project and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.