Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis is a process mediated by a specialised group of innate immune cells called phagocytes, including neutrophils, monocytes and macrophages. Phagocytosis is an essential process to maintain tissue homeostasis.
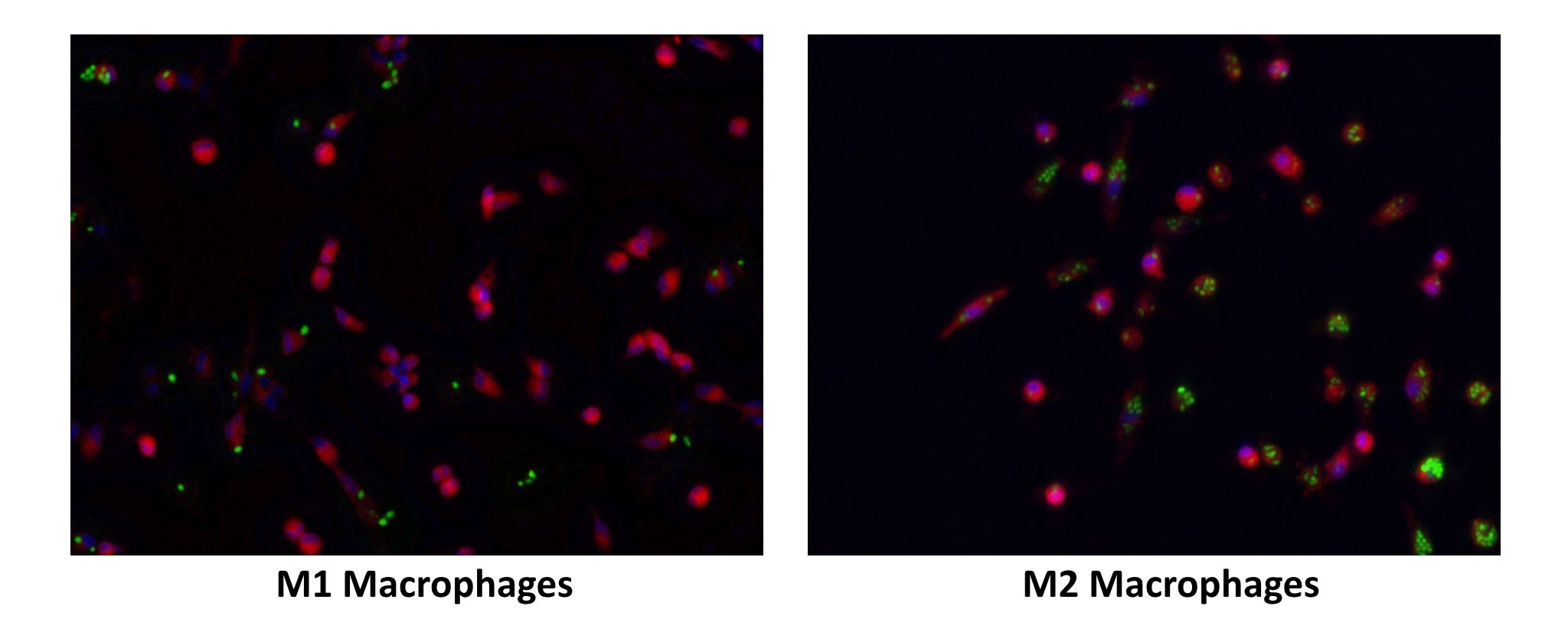
Primary monocytes (CD14+) isolated from PBMCs of healthy donors were subject to treatment with M-CSF for 6 days to induce M0 macrophage formation. On day 6, the naïve macrophages were exposed to either GM-CSF or IFNγ + M-CSF to generate M1 and M2 macrophages (MΦ) respectively. These cells were then exposed to fluorescent zymosan particles (green) and incubated for 3 hours to investigate the phagocytic effects of the polarised macrophages. After 3 hours, the cells were washed, stained with fluorescent membrane marker (red) and DAPI (blue) for nucleus.
Data suggests a higher phagocytic activity for M2 macrophages in this particular donor. (Objective= x20)

THP-1 cells treated with PMA for up to 3 days to induce mature macrophage phenotype. Cells were then exposed to fluorescent zymosan particles (green) and incubated for 3 hours to investigate their phagocytic effects. After 3 hours, the cells were washed, stained with fluorescent membrane marker (red) and DAPI (blue) for nucleus (Objective= x20).
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your phenotypic screening needs and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.