Respiratory Assays
Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis is an inflammatory disorder of the nasal mucosa induced by allergen exposure triggering IgE-mediated inflammation. It can also be associated with co-morbid conditions as Asthma, Atopic Dermatitis & Nasal polyps (Varshney et al., 2015).
Nasal Epithelial cells and PBMC Co-culture Allergic Rhinitis model: Inflammatory mediator expression
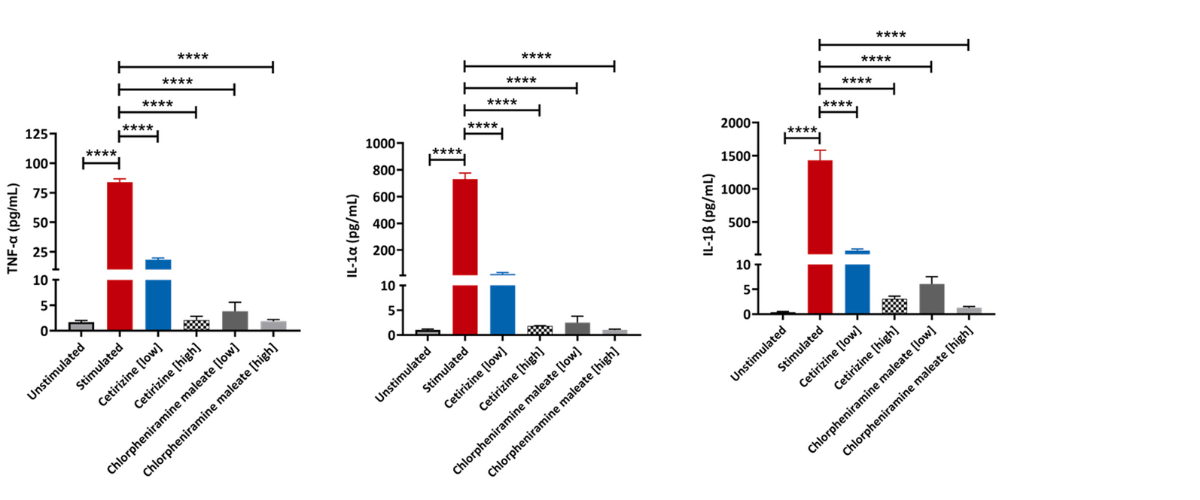
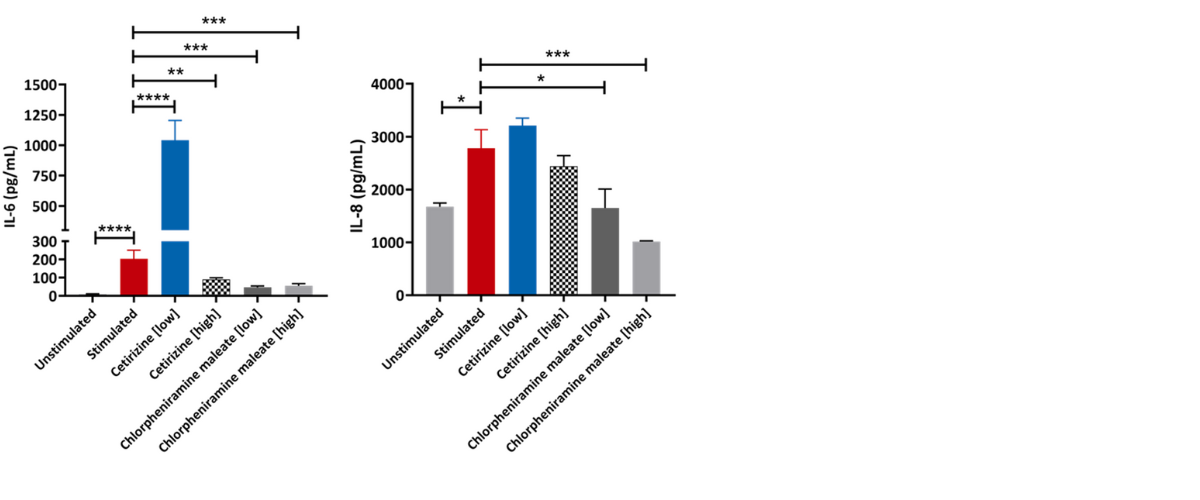
Figure 1. Effect of Cetirizine and Chlorpheniramine maleate on pro-inflammatory markers. RPMI 2650 cells differentiated for 21 days and freshly isolated PBMC cells were grown in co-culture. They were then stimulated with House Dust Mite Extract (HDME) to induce an allergic rhinitis phenotype in the presence or absence of a low and high concentration of the drugs. The levels of TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 released in the supernatants were determined using multiplex immunoassay technique. One-way ANOVA was performed to determine statistical significance (n=3±SEM; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001). Note: Unstimulated = RPMI 2650 + PBMCs, Stimulated = RPMI 2650 + PBMCs + HDME.
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your project and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.