Respiratory assays
Asthma/Airway Inflammation
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disorder arising from a poorly understood heterogenic gene-environment interaction. Characteristic features include variable airway obstruction and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. It is frequently known to coexist with atopic diseases, particularly allergic rhinitis. At Cellomatics we can offer a wide range of cellular models and readouts to address the main features of asthma and airway inflammation suitable for both early phase target identification and compound screening.
Human Airway Smooth Muscle cells stimulated with Poly I:C
The effect of PDE4 inhibitor on proinflammatory IL6 and IL8 release from Poly I:C stimulated Human Airway Smooth muscle cells (HASMs) was assessed. Poly I:C mimics viral infection and activates TLR3 receptors. HASMs were pretreated with the PDE4 inhibitor (1 nM) for 1 hour prior to stimulation with Poly I:C (10 µg/ml) for 24 hours. Cell culture supernatants were then collected and analysed for IL6 and IL8 release by ELISA (n=3±SEM; **p < 0.01).
Human Lung Fibroblasts stimulated with Poly I:C
Primary human lung fibroblasts were treated with TLR3 antagonists in conjunction with Poly I:C stimulation for 48 hours. The levels of IL-6, IL-8 (proinflammatory) and MCP-1 (chemokine involved in attracting monocytes and macrophages in inflammation) released in the supernatants were determined using Luminex Multiplex assay. One-way ANOVA was performed to determine statistical significance (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p <0.001).
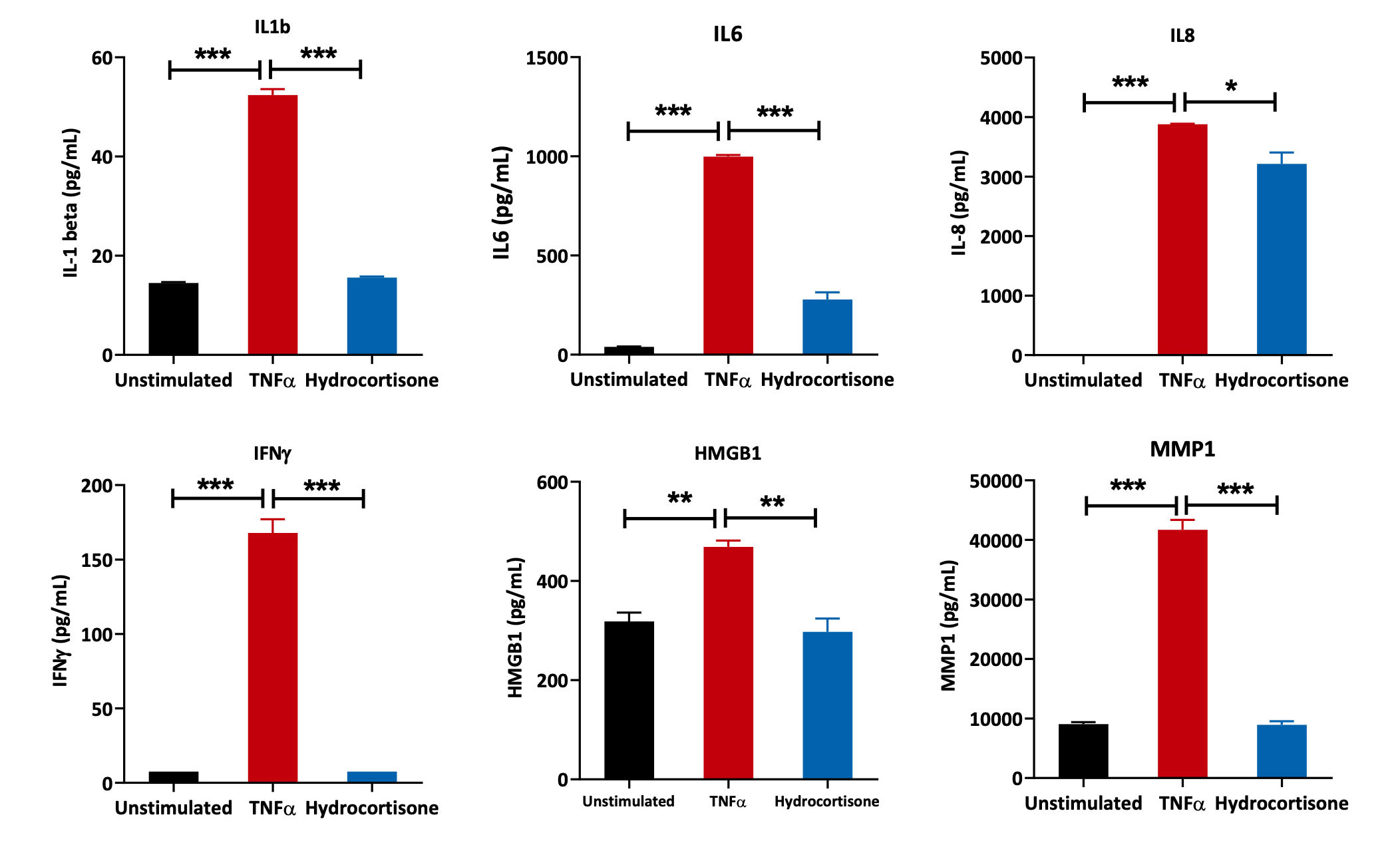
Human Lung Fibroblasts stimulated with TNFα
Primary human lung fibroblasts were treated with reference compound – Hydrocortisone in conjunction with TNF-α-mediated stimulation (to induce inflammation) for 48 hours. Expression levels of the proinflammatory mediators IL1β, IL6, IL8, IFNγ, MMP1 and HMGB1 were determined using an ELISA-based assay. One-way ANOVA was performed to determine statistical significance (*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p <0.001).
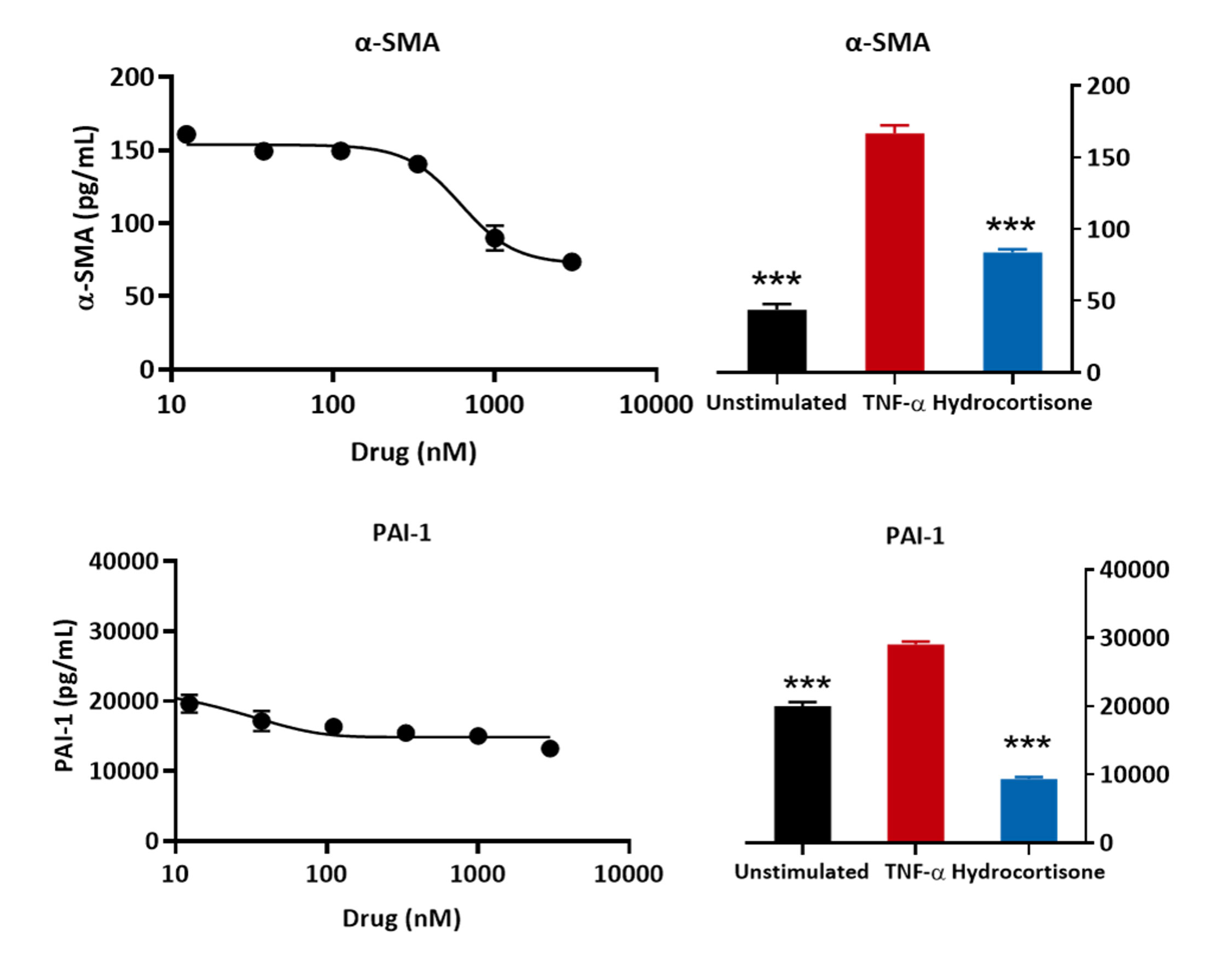
Primary human lung fibroblasts were pre-treated with the test and reference compound (hydrocortisone) followed by stimulation with TNFα for 48 hours. Expression levels of PAI-1 and a-SMA were determined using an ELISA-based assay. TNFα stimulation upregulated PAI-1 (an inhibitor of the fibrinolytic system and is increased in asthma) and α-SMA levels (modelling fibroblast-myofibroblast transition) and this was inhibited by hydrocortisone. (***p <0.001; n=3±SEM).
Collagen Gel contraction
Human airway smooth muscle cells were embedded within collagen and pre-treated with 2,3 BDM followed by incubation for 4 hours with Carbachol. Carbachol stimulates the muscle and hence the collagen gel to contract. Images were captured every 30 mins over a period of 3 and a half hours. Percentage change in gel contraction was then determined. For each treatment the percentage change in the gel contraction was calculated based on the values obtained at time 0. Each condition is representative of 3 biological replicates (n=3); mean+SEM. Data analysis was performed using the 2-WAY ANOVA analysis, *p<0.05; **p<0.01, ***p<0.0001; Carbachol vs. test ingredients groups.
Human Lung Fibroblasts stimulated with LPS
Primary Human Lung Fibroblasts were treated with 10 µg/ml LPS for 24 hours in the presence or absence of reference compound (hydrocortisone). Cell culture supernatants were then collected and levels of the proinflammatory IL6 and IL8 measured by ELISA (n=5±SEM; *p<0.05; **p<0.01).
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your project and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.