Immuno-oncology Assays
Immune Cell Killing
Natural killer cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) perform complementary roles in immune responses directed against viruses and tumours. CTLs are antigen specific and recognize peptides derived from virus and tumour antigens presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. NK cells can recognize and kill cells that have down-regulated MHC class I molecules from their cell surface. The major cytotoxic proteins contained within secretory lysosomes in NK cells and CTLs are the granzymes and perforin. Target cell recognition induces secretory lysosome exocytosis and the release of the cytotoxic contents of this organelle. Perforin then facilitates the entry of the granzymes into the target cell cytoplasm, where they cleave a variety of targets, such as caspases, resulting in cell death (Topham and Hewitt, 2009).
Our scientific team can test the efficacy of your compounds/biologics in relation to their ability to potentiate/facilitate tumour cell killing by immune cells including T cells, NK cells, PBMCs
Immune cell killing - MCF7 spheroids/T cells

Assessment of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity towards MCF-7 3D cancer spheroids. A schematic workflow applied to co-culture 3D cancer spheroids and primary human pan T cells to assess T cell-mediating killing of cancer cells.

Assessment of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity towards MCF-7 3D cancer spheroids. Unlabelled or labelled MCF-7 cancer cells were seeded into ultra low attachment (ULA) plates and cultured for 5 days prior to co-culture to facilitate 3D spheroid formation. Primary human Pan T cells were isolated from healthy donor blood and cultured for 24 hours in appropriate media with or without anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 stimulation antibodies prior to co-culture. Pan T cells were harvested and counted before being seeded into the ULA plates either alone or in co-culture with the MCF-7 3D spheroids at 10:1 and 20:1 Effector:Target ratios. T cell-mediated cytotoxicity was then assessed by performing the CellTiter-Glo® 3D Cell Viability Assay and measuring the luminescent signal on the GloMax® Discover Microplate Reader. Doxorubicin (50 μM), known to induce MCF-7 cancer cell death, was used in this assay as a positive control for cancer cell death. The percentage viability of 3D spheroids is shown for 24 hours and 48 hours post co-culture.
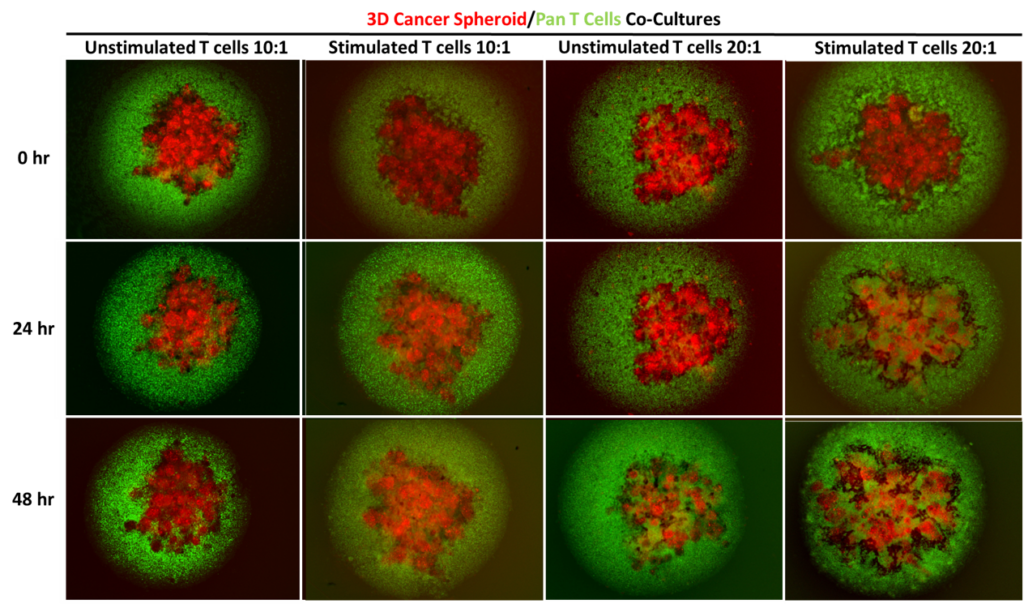
Assessment of T cell-mediated cytotoxicity towards MCF-7 3D cancer spheroids. Unlabelled or labelled MCF-7 cancer cells were seeded into ultra low attachment (ULA) plates and cultured for 5 days prior to co-culture to facilitate 3D spheroid formation. Primary human Pan T cells were isolated from healthy donor blood and cultured for 24 hours in appropriate media with or without anti-CD3 and anti-CD28 stimulation antibodies prior to co-culture. Pan T cells were harvested and counted before being seeded into the ULA plates either alone or in co-culture with the MCF-7 3D spheroids at 10:1 and 20:1 Effector:Target ratios. T cell-mediated cytotoxicity was then assessed. Fluorescent images were taken at 0 hour, 24 hours and 48 hours post-culture to assess T cell migration into the MCF-7 3D spheroids. Pan T cells (green) seeded at 20:1 ratio displays greater infiltration into the MCF-7 3D spheroids (red) compared to those seeded at 10:1 ratio. Data were represented as the mean ± SEM of 3 independent experiments each with 3 replicates.
Immune cell killing - K562/NK cells
Quantification of Caspase 3/7 activity in a co-culture model of K562 cells incubated with unstimulated/stimulated primary CD56+ NK cells (**p<0.01; ***p<0.001; n=3 ± SEM). Staurosporine was used as a positive control.
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your project and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.