Inflammation Assays
Psoriasis
An inflammatory skin disorder, triggered or exacerbated by a number of genetic, environmental, or immunological factors. Characterised by
- hyperproliferation of keratinocytes,
- abnormal epidermal differentiation and
- infiltration of inflammatory cells.
We offer options of different cell-based approaches for our clients to choose from:
Primary human Keratinocyte/Immortalised keratinocyte cell line & blood cell models – monoculture or co-culture
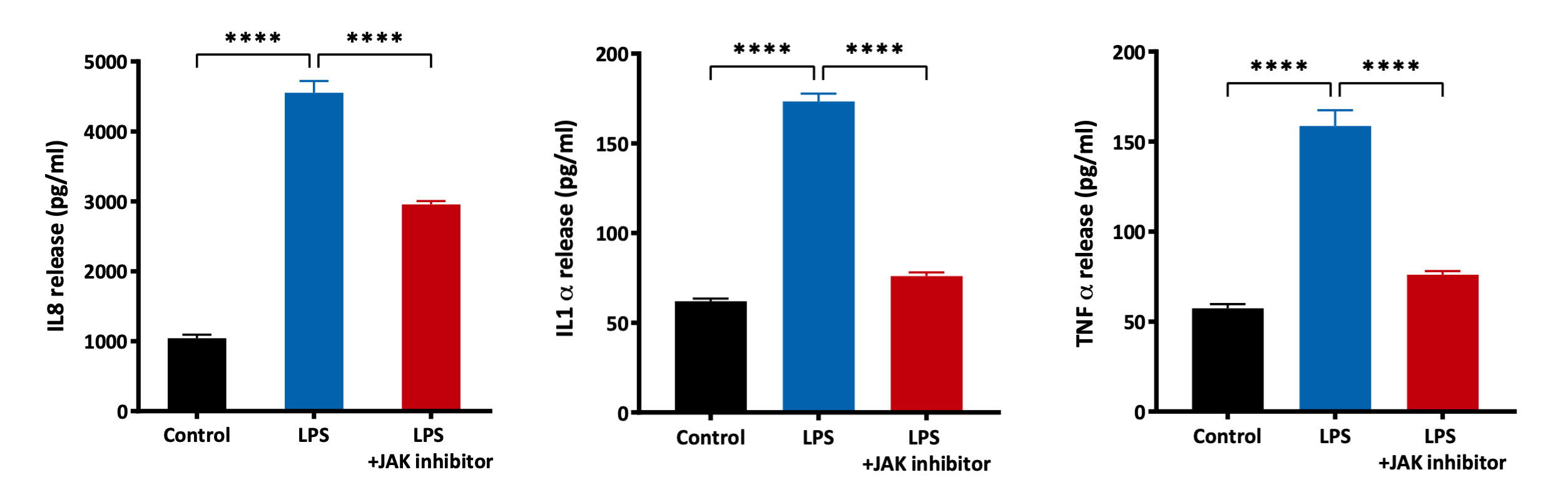
- Inflammation: Stimulation of cells with cytokine cocktail (IL1α + TNFα + Oncostatin M)
o Readout: IL8, GRO-alpha, IL6, IL4, IL22, IL12, IL23, TSLP, GM-CSF, IFN gamma
- Proliferation: Stimulation with cytokine
o Read out: BrdU, MTT, Alamar Blue, Ki-67, Caspase3/7
- Epidermal differentiation: Stimulation of cells with cytokine cocktail (IL1α + TNFα + Oncostatin M)
o Read out: mRNA levels of epidermal differentiation and tight junction protein markers
Primary human keratinocyte differentiation
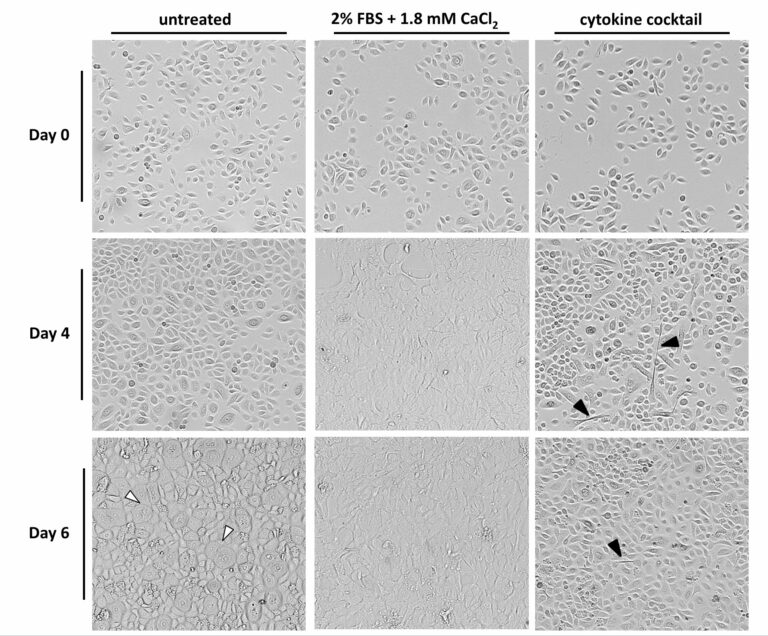
Keratinocyte differentiation was assessed following treatment with calcium + serum, treatment with a cytokine cocktail, or as a consequence of reaching high confluence (untreated). The majority of untreated control cells differentiated by day 6. Differentiated cells could be readily identified by their large size and cobblestone morphology (white arrows). Treatment with a combination of calcium and serum caused the keratinocytes to rapidly differentiate (>24 hours), resulting in flattened, fibrous, skin-like morphology which was sustained throughout the 6 days of treatment. The cytokine-treated cells (exposed to TNF-α, Oncostatin-M and IL1-α) seemed to exbibit delayed, aberrant differentiation, which is one of the hallmarks of psoriasis. Black arrows highlight irregular filament formation visible only in cytokine treated cells.
Keratinocyte Inflammatory Mediators
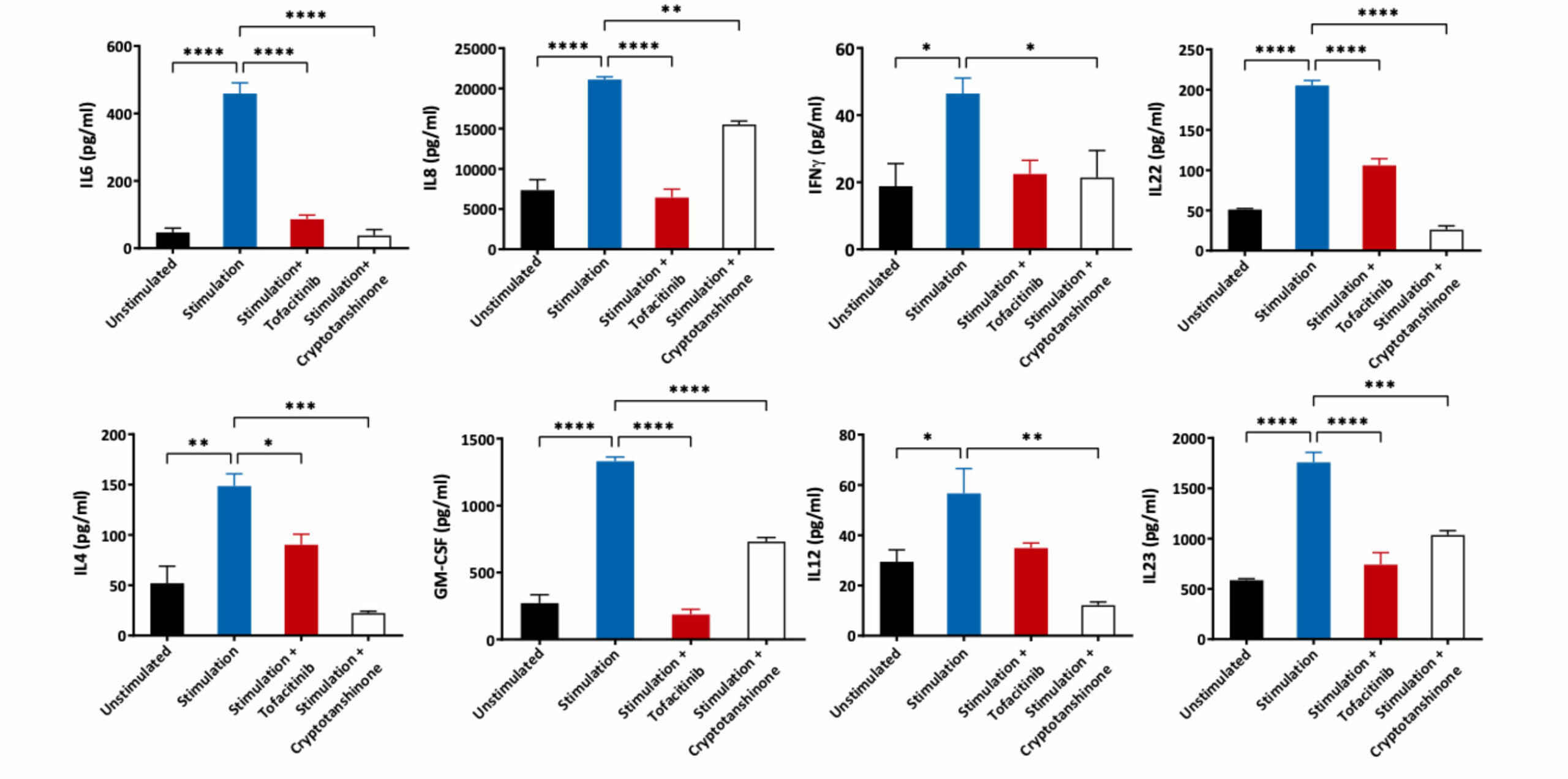
Human epidermal keratinocytes were differentiated in media supplemented with FBS and Calcium. The cells were then pre-treated with JAK3/STAT3 inhibitors followed by stimulation with a cytokine cocktail of IL1α + TNFα + Oncostatin M for 48 hours. Supernatants were analysed for various inflammatory mediators using Luminex Multiplex Assay (n=3±SEM;*p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001)
Keratinocyte Differentiation Markers
Human epidermal keratinocytes were allowed to differentiate in media supplemented with FBS and Calcium. The cells were then pre-treated with JAK3/STAT3 inhibitors followed by stimulation with a cytokine cocktail of IL1α + TNFα + Oncostatin M for 48 hours. Gene expression levels of key differentiation markers were analysed using Luminex Quantigene™ Assay. The mRNA expressions are normalised to GAPDH and fold change calculated relative to the unstimulated control (n=3±SEM; *p<0.05;**p<0.01;***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001).
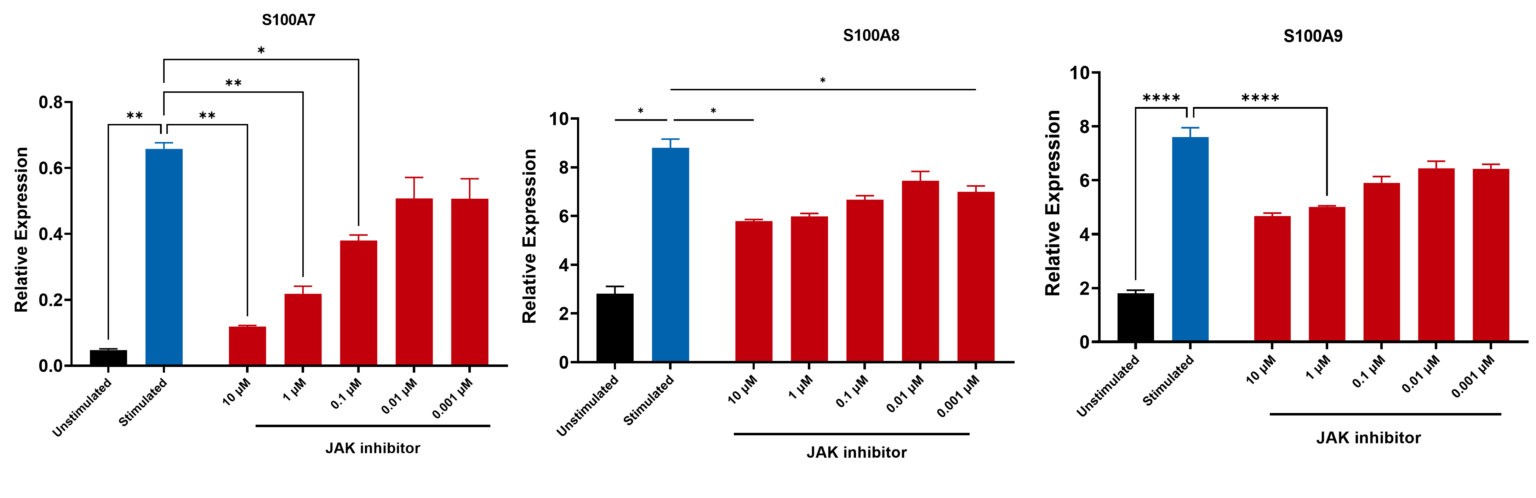
Human epidermal keratinocytes were allowed to differentiate. The cells were then pre-treated with JAK3 inhibitors followed by stimulation with a cytokine cocktail of IL1α + TNFα + Oncostatin M for 48 hours. Gene expression levels of key differentiation markers were analysed using Luminex Quantigene™ Assay. The mRNA expressions are normalised to GAPDH and fold change calculated relative to the unstimulated control (n=3±SEM; *p<0.05;**p<0.01;***p<0.001; ****p<0.0001).
Psoriasis: Proliferation in vitro model
Healthy Human epidermal keratinocytes were stimulated with recombinant IL17A and cultured in the presence or absence of STAT3 Inhibitor (Cryptotanshinone) for 5 days. A BrdU incorporation assay was then performed and results are expressed as absorbance values (n=3, mean±SEM; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001).
Request a consultation with Cellomatics Biosciences today
Our experienced team of in vitro laboratory scientists will work with you to understand your project and provide a bespoke project plan with a professional, flexible service and a fast turnaround time.
To request a consultation where we can discuss your exact requirements, please contact Cellomatics Biosciences.